Canine Gallbladder Problems: Signs & Solutions
Canine gallbladder problems often manifest as inflammation or gallstones. Symptoms may include vomiting, jaundice, and abdominal pain.
Understanding gallbladder issues in dogs is crucial for pet owners. The gallbladder plays a vital role in digesting fats by storing bile. Problems can arise from infections, blockages, or underlying health conditions. Early detection is key to effective treatment and recovery.
Symptoms like loss of appetite, lethargy, or unusual behavior should prompt a vet visit. Routine check-ups can help catch these issues before they escalate. Pet owners should be aware of their dog’s diet, as certain foods may contribute to gallbladder problems. Knowledge of these conditions allows for better prevention and management, ensuring a healthier life for your furry friend.
Introduction To Gallbladder Issues In Dogs
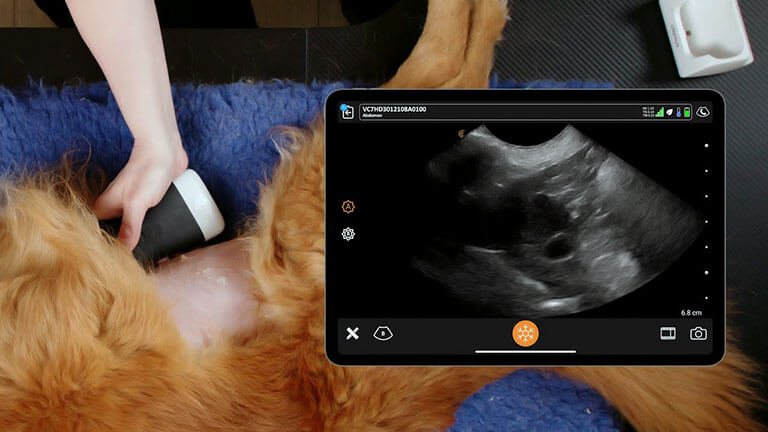
Gallbladder problems can affect your dog’s health. Understanding these issues helps in early detection. The gallbladder plays a crucial role in digestion. It stores bile, which helps break down fats. Knowing the symptoms can aid in prompt treatment.
The Role Of The Gallbladder
The gallbladder is a small organ located near the liver. It helps store bile produced by the liver. Bile is essential for digesting fats. Here are some key functions:
- Storage: Holds bile until needed.
- Concentration: Makes bile more potent.
- Release: Sends bile into the intestine during meals.
Gallbladder issues can disrupt these functions. This can lead to digestive problems in dogs.
Common Types Of Gallbladder Problems
Several gallbladder issues can affect dogs. Understanding these helps in recognizing symptoms.
| Gallbladder Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Cholecystitis | Inflammation of the gallbladder. |
| Gallstones | Hard deposits that form in the gallbladder. |
| Gallbladder Sludge | Thickened bile that can block bile flow. |
| Gallbladder Tumors | Abnormal growths that can affect function. |
Each of these conditions has unique symptoms. Monitoring your dog’s health can help in early intervention.
Early Signs Of Gallbladder Problems
Recognizing the early signs of canine gallbladder problems is crucial for your dog’s health. Early detection can lead to better treatment options. Dogs often show subtle symptoms that owners might overlook.
Changes In Appetite
One of the first signs of gallbladder issues is a change in appetite. Dogs may eat less or refuse food altogether. You might notice:
- Sudden loss of interest in food
- Increased thirst
- Picky eating habits
These changes can indicate discomfort or pain. Always monitor your dog’s eating patterns closely.
Vomiting And Diarrhea
Vomiting and diarrhea are common signs of gallbladder problems. These symptoms can appear suddenly. Watch for:
- Frequent vomiting
- Loose or watery stools
- Dark or bloody diarrhea
These issues may lead to dehydration. Keep your dog hydrated and consult a vet promptly.
Abdominal Pain And Discomfort
Abdominal pain is another critical sign. Your dog may exhibit several behaviors, such as:
- Whining or whimpering
- Restlessness or pacing
- Refusing to be touched around the abdomen
Examine your dog’s belly for swelling or tenderness. A visit to the vet is essential if symptoms persist.
Diagnosing Gallbladder Issues
Diagnosing gallbladder problems in dogs is crucial for their health. Early detection can lead to better treatment outcomes. Vets use various methods to identify these issues effectively.
Blood Tests And Their Importance
Blood tests help assess a dog’s overall health. They can reveal liver function and gallbladder issues. Key markers to watch include:
- ALT: Indicates liver cell damage.
- ALP: Shows bile duct problems.
- Bilirubin: Elevated levels suggest gallbladder issues.
Regular blood tests can catch problems early. Vets use these results to guide further tests.
Imaging Techniques: Ultrasound And X-rays
Imaging plays a vital role in diagnosing gallbladder problems. Two common techniques are:
| Technique | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Visualizes gallbladder size and structure. |
| X-rays | Helps identify stones or blockages. |
Ultrasound is non-invasive and provides real-time images. X-rays offer a different view but may require sedation.
When To Opt For A Biopsy
A biopsy may be necessary to confirm gallbladder disease. Vets recommend a biopsy if:
- Blood tests show abnormal results.
- Imaging reveals suspicious masses.
- Symptoms persist despite treatment.
A biopsy helps determine the type of disease. It provides essential information for treatment options.
Traditional Treatment Options
Canine gallbladder problems can cause discomfort and health issues for dogs. Traditional treatment options focus on relieving symptoms and addressing the underlying problems. Here, we explore three primary approaches: surgical interventions, medications, and dietary changes.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is often necessary for severe gallbladder issues. Here are key points about surgical options:
- Cholecystectomy: This surgery removes the gallbladder. It is common for gallbladder disease.
- Risks: Like any surgery, risks include infection and bleeding.
- Recovery: Dogs may need a few weeks to recover fully.
Medications For Managing Symptoms
Medications help control symptoms and improve your dog’s comfort. Common medications include:
- Anti-nausea drugs: These reduce vomiting.
- Pain relievers: They help manage discomfort.
- Antibiotics: Used for infections in the gallbladder.
Always consult a veterinarian before giving any medication. Proper dosage is essential for safety.
Dietary Changes And Their Impact
Diet plays a vital role in managing gallbladder problems. Consider these dietary changes:
- Low-fat diets: Reducing fat intake can ease gallbladder stress.
- High-fiber foods: Fiber aids digestion and overall health.
- Hydration: Ensure your dog drinks plenty of water.
Consult with a vet for specific dietary recommendations. A tailored diet can enhance recovery.
Non-traditional Remedies And Supplements
Canine gallbladder issues can be tough to manage. Many pet owners seek non-traditional remedies and supplements. These alternatives may support liver and gallbladder health. They can also help reduce symptoms. Here are some popular options to consider.
Herbal Supplements
Herbal supplements are a popular choice. They can support gallbladder function in dogs. Some effective herbs include:
- Milk Thistle – Protects the liver and promotes detoxification.
- Dandelion Root – Supports bile production and digestion.
- Turmeric – Has anti-inflammatory properties that can aid gallbladder health.
Always consult a vet before starting herbal treatments. Dosage can vary based on your dog’s size and health status.
Homeopathic Approaches
Homeopathy focuses on gentle healing. It uses small doses of natural substances. Here are some remedies that may help:
- Carduus Marianus – Supports liver function.
- Berberis Vulgaris – Aids in bile flow and digestion.
- Cholesterinum – Helps manage cholesterol levels.
Consult with a certified homeopathic vet for the best results.
Diet Supplements And Probiotics
Diet plays a crucial role in gallbladder health. Certain supplements can enhance your dog’s diet:
| Supplement | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Reduce inflammation and support overall health. |
| Probiotics | Promote healthy gut bacteria and digestion. |
| Digestive Enzymes | Aid in food breakdown and nutrient absorption. |
Adding these supplements can improve your dog’s digestive health. Always check with your vet before making changes to their diet.
Dietary Management And Prevention
Managing your dog’s diet can help prevent gallbladder problems. Proper nutrition supports liver and gallbladder health. A well-balanced diet reduces the risk of stones and other issues.
Foods To Include
Choosing the right foods can make a big difference. Include these options in your dog’s diet:
- Lean proteins: Chicken, turkey, and fish are great choices.
- Fruits: Blueberries and apples provide vitamins and antioxidants.
- Vegetables: Carrots and green beans are low in fat.
- Whole grains: Brown rice and oats offer fiber and energy.
- Healthy fats: Fish oil can support gallbladder function.
Foods To Avoid
Certain foods can harm your dog’s gallbladder. Avoid these:
- High-fat foods: Fried foods can lead to gallbladder issues.
- Processed foods: They often contain unhealthy additives.
- Rich table scraps: Foods meant for humans may upset their stomachs.
- Chocolate and caffeine: These are toxic for dogs.
- Excessive dairy: Can cause digestive problems.
The Importance Of Hydration
Hydration plays a key role in your dog’s health. Ensure your dog drinks enough water daily. Proper hydration helps the gallbladder function smoothly. Here are some tips:
- Provide fresh water at all times.
- Encourage drinking during meals.
- Consider adding water to dry food.
- Monitor water intake, especially in hot weather.
Recovery And Post-treatment Care
After treatment for canine gallbladder problems, proper care is vital. This ensures your dog heals well. You must monitor their health closely. Adjustments in diet and activity levels are necessary. Let’s explore these aspects of recovery.
Monitoring For Potential Complications
Keep an eye on your dog’s health after treatment. Watch for signs of complications:
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Lethargy
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
If you notice any of these symptoms, contact your vet. Regular check-ups help catch issues early. Schedule follow-up appointments as advised.
Adjusting Your Dog’s Diet Post-treatment
A proper diet is crucial for recovery. Your vet may recommend a special diet. Focus on these dietary changes:
| Food Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Low-fat foods | Reduces gallbladder strain |
| Easily digestible proteins | Supports recovery |
| High-fiber foods | Improves digestive health |
Introduce new foods gradually. Monitor your dog for any adverse reactions. Keep water fresh and available at all times.
Physical Activity And Rest
Balancing activity and rest is important. Your dog needs gentle exercise. Avoid strenuous activities initially. Consider short walks and playtime.
- Limit playtime to 10-15 minutes.
- Avoid jumping or running.
- Gradually increase activity as your dog heals.
Rest is equally vital. Create a comfortable space for your dog. Ensure they have a quiet area to relax. Monitor their energy levels closely.
Case Studies And Success Stories
Understanding canine gallbladder problems requires real-life examples. These case studies highlight recovery journeys, treatment methods, and long-term management. Each story brings hope and insight for dog owners.
Recovery Journeys Of Different Breeds
Different breeds face unique challenges with gallbladder issues. Here are three inspiring recovery stories:
- Labrador Retriever: Max had gallstones. After surgery, he regained energy. His owners followed a strict diet.
- Beagle: Bella suffered from gallbladder inflammation. With medication and diet changes, she returned to her playful self.
- Golden Retriever: Charlie faced severe bile duct obstruction. Surgery and a tailored diet improved his condition significantly.
Comparative Analysis Of Treatment Methods
Various treatment options exist for gallbladder problems. Here’s a comparison of common methods:
| Treatment Method | Effectiveness | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery | High | 2-4 weeks |
| Medication | Moderate | Ongoing |
| Dietary Changes | Variable | Ongoing |
Long-term Health Management Post-recovery
After recovery, maintaining your dog’s health is crucial. Here are key practices:
- Regular Vet Check-ups: Schedule check-ups every six months.
- Healthy Diet: Choose low-fat, high-quality food.
- Weight Management: Keep your dog’s weight in check.
- Monitor Symptoms: Watch for signs of discomfort or illness.
- Exercise: Ensure daily walks and playtime.
These steps support your dog’s ongoing health and happiness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Common Signs Of Gallbladder Issues In Dogs?
Symptoms may include vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and abdominal pain. Look for lethargy and jaundice as well.
How Are Gallbladder Problems Diagnosed In Dogs?
Veterinarians typically use blood tests, ultrasounds, and X-rays to diagnose gallbladder issues effectively.
What Causes Gallbladder Problems In Dogs?
Gallbladder issues can stem from infections, tumors, or bile duct obstructions. Diet and genetics may also play a role.
What Treatments Are Available For Canine Gallbladder Problems?
Treatment options include dietary changes, medications, or surgery, depending on the severity and underlying cause.
Can Gallbladder Problems Lead To Serious Conditions?
Yes, untreated gallbladder issues can result in pancreatitis, liver damage, or even life-threatening infections in dogs.
Conclusion
Canine gallbladder problems can significantly impact your dog’s health. Early detection and treatment are crucial for a positive outcome. Regular vet check-ups can help identify issues before they escalate. Always monitor your dog’s symptoms closely. With proper care, many dogs can lead happy, healthy lives despite gallbladder concerns.
Prioritize your pet’s health today.






